One of the many repercussions from the COVID-19 pandemic was a world-wide hit to students’ health and wellbeing. In particular, proper nutrition and food insecurity was greatly affected by the pandemic and the lockdowns as many students around the world could not get food and food related support at their schools. In Part 1 of this two part series, Sierra Bickford takes stock of the impact school nutrition programs have globally and highlights the effects of these high-impact interventions. Part 2 will scan recent news and research to find some of the many micro-innovations – new developments in practices, structures, and resources in different contexts – that have been implemented to combat this rise in student food insecurity. These posts are part of IEN’s ongoing coverage of what is and is not changing in schools and education following the pandemic school closures. For more on the series, see “What can change in schools after the pandemic?” For related examples of micro-innovations in other areas, see IEN’s coverage micro-innovations to strengthen student relationships, to increase access to college and careers and to improve tutoring: Building Student Relationships Post-Pandemic in School and Beyond; Still Worth It? (Part 1); New Pathways into Higher Education and the Working World? (Part 2); Tutoring takes off and Predictable challenges and possibilities for effective tutoring at scale.
Food insecurity, particularly among children, was one of the critical problems exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic and the related societal shutdowns. Estimates suggest that, during the pandemic, the number of people experiencing food insecurity doubled from about 135 million to more than 270 million. In India alone, household food insecurity skyrocketed from 21% in December 2019 to 80% in August 2020, at the same time that diet quality decreased. By the end of 2021, the UN warned that over 43 million people in 38 countries, including Ethiopia, Somalia, South Sudan, Afghanistan, and Yemen, were at risk of experiencing famine or famine-like conditions.
“Estimates suggest that, during the pandemic, the number of people experiencing food insecurity doubled from about 135 million to more than 270 million.”
Even in wealthier countries household food insecurity increased substantially. In the United States, that meant a rise in households experiencing food insecurity from 11% in 2018 to 38% in March 2020. In a report from 2020, the US Census’s Household Pulse Survey estimated the rates of food insecurity had doubled overall, and tripled among households with children. In the wake of the pandemic, school systems, despite vastly different conditions and challenges in different contexts, are working to reestablish nutrition programs and create new strategies to get children access to nutritious balanced meals.
The impact of school based nutrition worldwide
Across the world, school meals have been shown to be a worthwhile intervention with high positive impact on health and learning outcomes. In high income countries, such as those in the United Kingdom, access to nutritious school meals are associated with lower obesity rates. In Sweden, school meals with regulated nutrition requirements have been shown to increase educational attainment, health outcomes, and income across lifetime. One study found that low income families with children in Sweden who received free school meals increased their lifetime income by 6%. The effects that these interventions have on European health care costs estimate “that the return from investment in school meal programs is at least sevenfold, up to a possible €34 for every €1 spent.”
“The effects that these interventions have on European health care costs estimate “that the return from investment in school meal programs is at least sevenfold, up to a possible €34 for every €1 spent.”’
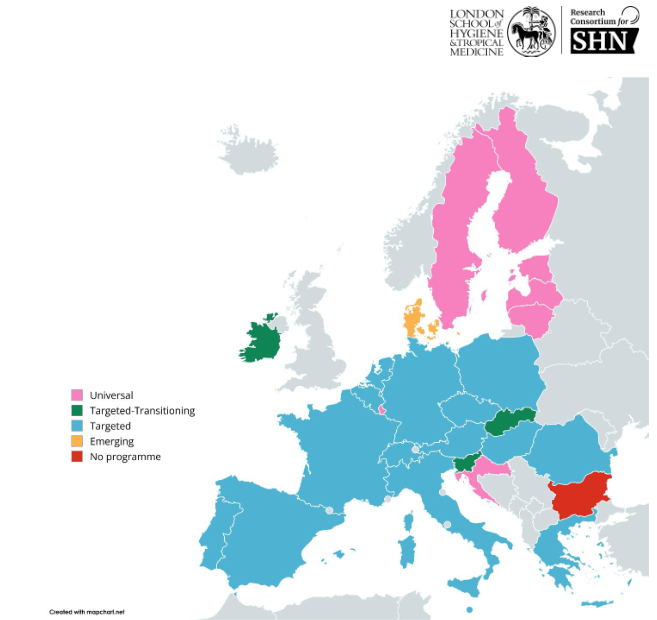
Data from low and middle income countries also support the implementation of free school meals, particularly for increasing attendance and retention. In Burkina Faso female students who were given take-home food attended school at least 90% of the time. Similarly in Bangladesh, the introduction of free fortified biscuits “increased enrollment by 14% and reduced school dropout by 7%.” Nutrition programs in low and middle income countries have been shown to positively affect learning outcomes as well. In India, access to free school meals is associated with higher cognitive outcomes and an 18% increase in literacy test scores. As in the United Kingdom, in Brazil students who were being supplied meals at school were more likely to reduce their intake of unhealthy foods and increase the presence of nutritious food in their diet, which leads to better health outcomes.
The impact of school based nutrition in the United States
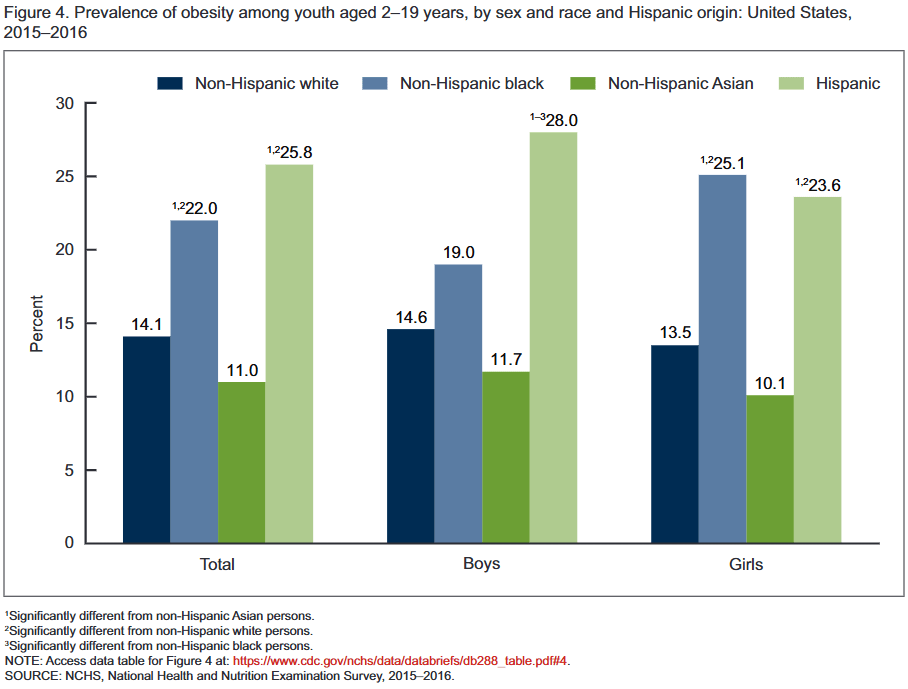
In the US, the National School Lunch Program has long been the primary vehicle for supporting students’ nutritional needs. Around 95% of US elementary, middle, and high schools take part in the program and about 75% of the meals provided through it go to children from low-income families who qualify for free or reduced-price lunches. Students who consistently consumed these meals were more often from low-income households and more likely to be non-Hispanic Black or Hispanic compared to those who didn’t participate. As a consequence, the program is one key means of addressing nutritional and health inequalities in the US, where non-Hispanic black and Hispanic children are more likely to be overweight or obese and have lower quality diets than white children.
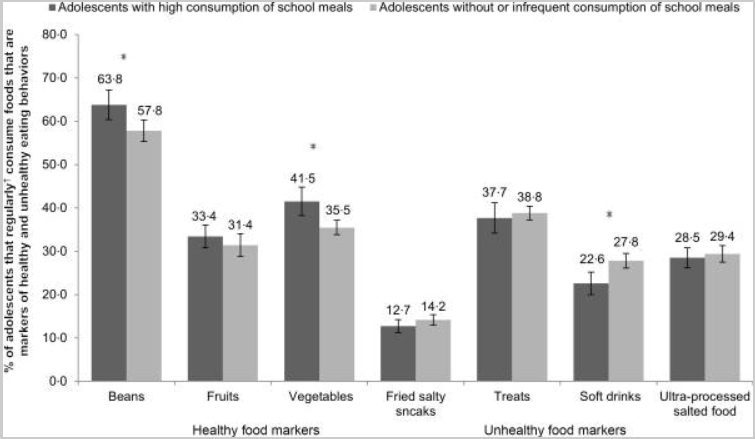
In fact, US students who eat school meals daily ate less saturated fat and sugar than students not eating school meals and had less prevalence of obesity. In addition, in the US, school meals help to reduce food insecurity, and, in some cases, provide up to half of a child’s daily energy intake. Studies from the US show that left unaddressed, food insecurity and a lack of nutritious food can interfere with students academic and cognitive development and can have a negative impact on their social development and behavior in school.
Despite this evidence, the budget bill promoted by the US administration and passed by Congress this past summer reduces funding for federal health and food programs. Estimates from the School Nutrition Association suggest that the bill could create a ripple effect of food insecurity for American children. This ripple effect will include fewer children automatically being eligible for SNAP and school lunch programs as well as fewer schools being able to enroll in Community Eligibility Provision. Nonetheless, even as these cuts are being made, schools and communities across the US and around the world are continuing to develop new ways of reaching more and more children and families and increasing access to higher quality and healthier food.
Next Week: Innovations in providing children with food and nutrition: Scanning the headlines for new ways to support students’ health and wellbeing after the pandemic (Part 2)