To get a glimpse of Japan’s effort to create a “child-centered society,” Hirokazu Yokota shares what he’s learned from his experiences working at the Children and Families Agency (CFA). In the first part of this 3-part interview, Yokota describes the establishment of the CFA and the efforts to promote digital transformation in childcare. Parts 2 and 3 discuss the current initiatives of the CFA and Yokota’s personal reflections on his involvement in the development of new governmental institutions in Japan. Yokota has followed a rare career path as a bureaucrat who belongs to the Japanese Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT), but who has repeatedly stepped out of the “education circle” to work in other agencies, including the Children and Families Agency, which was established in April 2023. In 2021, Yokota was also one of the charter members helping to establish Japan’s Digital Agency , and he went on to work as a Deputy Superintendent in Toda City. Yokota has previously written about his experiences as a parent and educator during the pandemic as well as his work as a government official and administrator in: A view from Japan: Hirokazu Yokota on school closures and the pandemic; Hiro Yokota on parenting, education and the new Digital Agency in Japan; and Hirokazu Yokota on aggressive education reforms to change the “grammar of schooling” in Toda City (part 1) and (part 2). Please note that Yokota is sharing his personal view on CFA and its policies, and his views do not represent the official views of the government. For further information contact him via Linkedin.
IEN: Can you tell us a bit about the Children and Families Agency and why it was established?
Hiro Yokota: The Basic Policy on the New Framework for Promoting Child Policy – Establishment of the Children and Families Agency Aimed at Realizing a Child-Centered Society (Cabinet decision, December 21, 2021) stated a clear rationale for establishing this new agency:
“Now more than ever, we are at a critical crossroads: we must strongly advance child-related policies not only to curb the declining birthrate, but also to enhance the well-being of every child and ensure the sustainable development of society. With the best interests of the child always as the top priority, we aim to place children and child-related policies at the very heart of our society—an approach referred to as a “child-centered society” (kodomo mannaka shakai). From the perspective of children, we will take into account all environments surrounding them, guarantee their rights, and ensure that no child is left behind. As a society, we will support their healthy growth collectively. To realize this vision of a child-centered society, we are establishing a new central governing body: the Children and Families Agency (Kodomo Katei-chō).”
Based on this basic policy, the Basic Act on Children’s Policy and the Act Establishing the Children and Families Agency were submitted to and passed the Japanese Diet in June 2022, about one year prior to the establishment of the CFA (April 2023).
IEN: How did you come to work at the Children and Families Agency?
HY: From April 2022 to March 2024, I served as a deputy superintendent and director for education policy at Toda City Board of Education Office in Saitama prefecture. More than three years had passed since I left my home ministry – the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT) – so most everyone anticipated I would return to MEXT, as I mentioned in my previous article. However, that did not happen, and I was seconded again, this time to CFA, which was actually what I wished for. In order to change and make education better, I take a stance of getting intentionally out of the “education village” and trying to change the status quo from outside.
IEN: Could you provide some examples of your primary work at the Children and Families Agency?
HY: My division (Childcare Policy Division, Child Development Bureau) is mainly in charge of three policies related to early childhood education and care; connecting children to the childcare system; increasing support for childcare workers; and promoting the digital transformation in childcare.
Free Early Childhood Education and Care
In light of the need to address Japan’s declining birthrate and recognizing the vital role early childhood education plays in personality development and forming the foundation for compulsory education, the government introduced free early childhood education and care in October 2019. Under this initiative — as explained in the English-language pamphlet “What about my child?”— all children aged 3 to 5 can attend nursery schools, certified child centers (nintei kodomoen), or kindergartens free of charge. For children aged 0 to 2, households exempt from resident tax are eligible for free care. Others have to pay a fee for their first child, but the second child in the household receives a 50% reduction in fees, and care is fully subsidized for third and subsequent children.
According to the “Children’s Future Strategy” (Kodomo Mirai Senryaku), approved by the Cabinet on December 22nd 2023, many families — especially those with children aged 0 to 2, of whom about 60% are not enrolled in formal childcare — face anxiety and isolation in childrearing. In response, the government aims to support all children and families regardless of work status or lifestyle by enhancing access to high-quality early childhood environments. To achieve this, a new benefit called the Connecting All Children to ECEC System was established, allowing flexible, hourly use of childcare services within a monthly usage limit, without employment-related requirements.
“a new benefit called the Connecting All Children to ECEC System was established, allowing flexible, hourly use of childcare services within a monthly usage limit“
Improving Compensation and Staffing for Childcare Workers
To attract and retain dedicated childcare professionals, enhancing their working conditions is essential. As part of this effort, the FY2024 and FY2025 supplementary budget includes a significant 10.7% increase in personnel costs and, since 2012, total improvements have amounted to approximately 34%. While the average salary still lags behind that of all industries, the government’s recently published “New Directions in Childcare Policy” outlines a clear goal of achieving parity with national averages. Staffing standards are also being revised to improve safety and quality of childcare. For the first time in 76 years, the staff-to-child ratio for 4- and 5-year-olds is being improved from 1:30 to 1:25 through a new Enhanced Staffing Subsidy. Additionally, for the first time in over 50 years, for 1-year-olds a new subsidy has been introduced for facilities improving staffing from 1:6 to 1:5. To ensure that these improvements actually reach childcare sites, the revised Act on Child and Childcare Support also mandates greater transparency in financial operations. Childcare providers must annually report their staffing levels, salary data, and income/expenditure details to prefectural governors, who will then disclose key figures — such as model salaries and labor cost ratios — at both individual and aggregate levels. This transparency will help guide future improvements in standardized pricing.
Promoting Digital Transformation (DX) in Childcare
Currently, both childcare facilities and local governments face substantial administrative burdens. Facilities must prepare numerous documents for subsidy applications and audits, with formats varying across municipalities. Local government staff spend considerable time manually entering and checking information submitted by facilities, often needing follow-up in cases of errors or omissions. Parents also face burdens, including time-consuming information gathering, the need to call during operating hours to schedule visits, and handwritten application forms submitted in person — even during pregnancy or while caring for young children.
To resolve these issues, the Agency aims to reduce reliance on analog documentation through digital data-sharing and thereby free up time for childcare professionals to focus on children. For local governments, the goal is to reduce the workload associated with data entry and review, allowing staff to focus on improving the quality of care. For parents, we are working toward a seamless, one-stop digital experience for all steps of the childcare application process.
“To resolve these issues, we aim to reduce reliance on analog documentation through digital data-sharing and thereby free up time for childcare professionals to focus on children.“
To that end, we are developing two key national platforms:
- The Facilities Administration Platform on Childcare Administrative Affairs, which supports “Once Only” data entry for subsidy and audit-related procedures through integration with facility ICT systems and government backend systems. This will reduce duplicate submissions and streamline communication between facilities and municipalities.
- The Information Linkage Platform for Childcare Activities, which connects parents, facilities, and local governments to enable end-to-end digital childcare procedures—such as information searches, visit reservations, and applications—via smartphone.
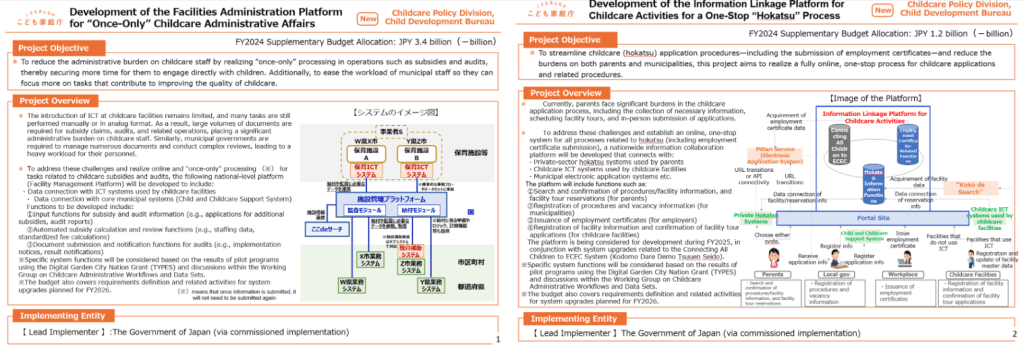
By the end of FY2025, we aim to begin pilot operations for both platforms with nationwide rollout planned from FY2026 onward. Through all of these efforts, we aim to create an environment where the benefits of digital transformation are clearly understood by those on the ground; that enhance the attractiveness of the childcare profession for future generations; and that ultimately make the system easier and more convenient for all stakeholders.
To accelerate the digital transformation in childcare, we also launched a new initiative in FY2024: the Childcare ICT Lab Program. This program supports model projects at multiple sites across Japan, implemented in partnership with private-sector entities.
Next Week: Centering Children and Youth in Policymaking: Hiro Yokota on the Development of a “Child-Centered Society” in Japan (Part 2)
