As we look back on 2025, we’d like to celebrate some of the extraordinary work in education we learned about this year. In this case, we’re highlighting the work of the Aspire Leadership Fellows of the Africa Leadership Academy. The Aspire Fellowship Programme is a cohort-based program that brings together leaders from across Africa who have started or are leading innovative schools and educational organizations. The Fellows work with global education leaders to expand and sustain their organizations. For those interested in learning more about this work or making a donation, we’re providing the Aspire profiles and websites of several of the Fellows who shared their work with graduate students from Teachers College, Columbia University, in Thomas Hatch’s class on School Change this fall.

Soofia International School
Butha, Buthe, Lesotho
Highlight: Running a lean Cambridge model at a community-funded school catering to children from diverse families in rural Lesotho- some facing significant socio-economic challenges and other instabilities
Year Founded: 1990
Grade: Nursery/Pre-Primary, Primary, Secondary, AS & A Level
School Vision: To deliver affordable, globally benchmarked education with a strong emphasis on equity, innovation, and holistic development.
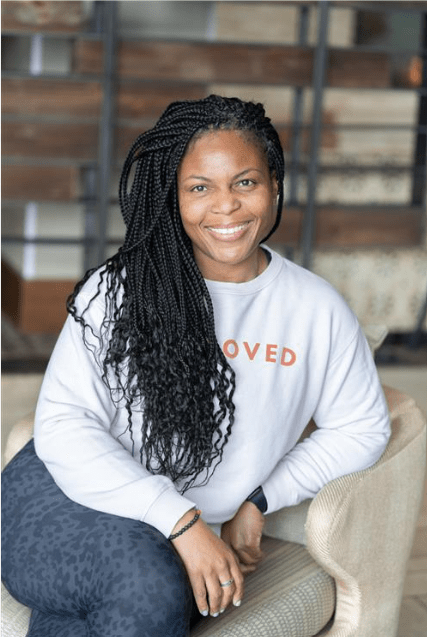
Jayant Vijayakumar is Chief Academic Advisor at Soofia International School in Lesotho, where he leads strategic planning, academic innovation, and AI integration. Under his leadership, Soofia—serving over 1,300 students—has embraced flipped learning, launched coding and robotics programs, and pioneered student-led engagement models. Jayant’s approach blends academic rigour with emotional intelligence, technology, and values-based education, ensuring access and excellence for learners from all backgrounds. He trains educators, drives curriculum reform, and builds partnerships that extend Soofia’s impact across Lesotho and beyond. Passionate about transforming outdated education systems, Jayant’s work is driven by a belief that inclusive, holistic education can empower the next generation of thinkers, leaders, and changemakers in Africa and the world. Donation/Support link
Planning for Tomorrow Youth Organization
P4T – Planning for Tomorrow Youth Organization
Kyangwali Refugee Settlement, Uganda
Highlight: Refugee-founded and refugee-led education which started with 26 students in a boardroom, and has grown to serve more than 800 students
Year founded: 2007
Grade Focus: K-12
School vision: A healthy and self-reliant community with knowledge and skills.
Daniel, also known as Khalid, is a Congolese Refugee who has resided in Uganda for the past 26 years. Leveraging the DAFI scholarship, Khalid earned an MS in Environmental Health and a Bachelor of Statistics Degree. He leads this refugee-led youth initiative dedicated to empowering vulnerable refugees and Ugandans towards becoming healthy and self-reliant. P4T Schools delivers comprehensive educational services, including improved teaching methodologies, a school feeding program, engaging children in debate, games, and sports. The overarching goal of these schools is to evolve into centers of excellence, with a focus on nurturing Innovative Leaders and Changemakers.
Kevin is an Education Coordinator and Early Childhood Development project manager at P4T. She attained a BS in Education under MasterCard Foundation Scholarship. She did teaching practice at Mandela Secondary school, taught at the North Green School and had a one-year volunteer experience as a teaching assistant at Lancaster Mennonite School in Pennsylvania, USA. Kevin uses her positive attitude to encourage others to work hard and bring about a positive impact in their communities. She is very passionate about giving back “because in one way or the other it is what made her who she is, a transformative leader.” Donation/Support link
Inmates Educational Foundation (IEF)

Inmates Educational Foundation
Nigeria (Lagos, Oyo, Osun, Kano, Abuja, and Ebonyi states)
Highlight: Running a school system in Nigerian correctional centers to provide access to formal and informal education as a form of reformation and reintegration for inmates.
Year Founded: 2018
Grade: Nursery/Pre-Primary, Primary, Secondary, National Open University
School Vision: To provide educational opportunities to inmates, empowering them to reintegrate into society and become productive citizens..
Mahfuz Alabidun is the Founder and Executive Director of Inmates Educational Foundation, a nonprofit delivering education in Nigerian correctional centers. With over 500 learners across six states, IEF offers academic, vocational, and reintegration programs that support inmates’ transformation and reintegration into society. Under his leadership, the foundation has received national recognition, including the Governor of Lagos State Social Impact Award. A TEDx speaker and education reform advocate, he is passionate about building inclusive systems that restore dignity and create second chances. Through education, Mahfuz is rewriting the narrative of incarceration in Nigeria—one learner, one center, one future at a time. Cohort 5 Year Founded: 2018 Grade: Nursery/Pre-Primary, Primary, Secondary, National Open University School Vision: To to provide educational opportunities to inmates, empowering them to reintegrate into society and become productive citizens. Donation/Support link
Humanitarian Services Action (HuSA)

Humanitarian Services Action (HuSA)
Kikuube, Uganda
Highlight: Running a school model that not only educates but also heals and empowers children, especially those affected by conflict, displacement, and poverty; with focus on Protection and Integrated Mental Health and Psychosocial Support Services (MHPSS).
Year Founded: 2020
Grade: Nursery/Pre-Primary, Primary
School Vision: To create a new generation of African leaders and change-makers who are self-reliant and capable of lifting others.
Sumi Hamid is a refugee leader and the Founder and Executive Director of Humanitarian Services Action Organisation (HuSA) in Kikuube, Uganda. A survivor of displacement himself, he grew up in Kyangwali Refugee Settlement and now leads community-based initiatives that provide education, mental health support, and protection services to refugee children and families. After overcoming years of interrupted education, Sumi pursued a career in social work and made the bold decision in 2023 to leave formal employment and fully commit to building HuSA. His organization now serves over 130 children with early education and supports women and youth with microgrants, GBV response, and psychosocial care. Rooted in lived experience, his work champions dignity, empowerment, and community-led change—offering vulnerable children and families the opportunity to learn, heal, and thrive. Cohort 5 Year Founded: 2020 Grade: Nursery/Pre-Primary, Primary School Vision: To create a new generation of African leaders and change-makers who are self-reliant and capable of lifting others. Donation/Support link

Ajibu Community
5Mayuge, Uganda
Highlight: They produce their own play-learning resources which are used to combine play-based learning interventions with life skills development, ensuring that children not only succeed academically but also explore their innate talents and build strong social-emotional and entrepreneurial skills to reach their full potential
Year Founded: 2021
Grade: Nursery/Pre-Primary, Primary, Vocational Training for mothers
School Vision: To create a model Play-Based Learning school in Eastern Uganda where education is focused on academic excellence and skills development so that there’s a clear path for every child to succeed in life.
Timothy David Wambi is the Founder of Ajibu Community Organisation (Ajco) in rural Mayuge, Uganda. Timothy leads grassroots education reform through a dual-impact model: supporting public primary schools and running a vibrant community learning center. Ajco currently educates 77 children aged 3–7 and empowers young women—many of them survivors of early marriage—to become trained educators. Timothy’s model integrates play-based, life-skills learning and develops low-cost teaching materials to improve literacy, numeracy, and STEM outcomes in under-resourced schools. Timothy works to ensure that no child is denied the right to quality education and that local solutions are part of lasting transformation in Uganda’s rural education landscape. Donation/Support link
Itinga Charity Education Foundation

Itinga Charity Education Foundation
Northern Uganda
Highlight: The only inclusive secondary school in Northern Uganda catering to students with diverse abilities such as the blind, low vision, cerebral palsy, intellectual disabilities, and physical challenged, studying alongside their abled peers.
Year Founded: 2024
Grade: Secondary
School Vision: To empower students to thrive, regardless of ability, and promotes a culture of acceptance and inclusion
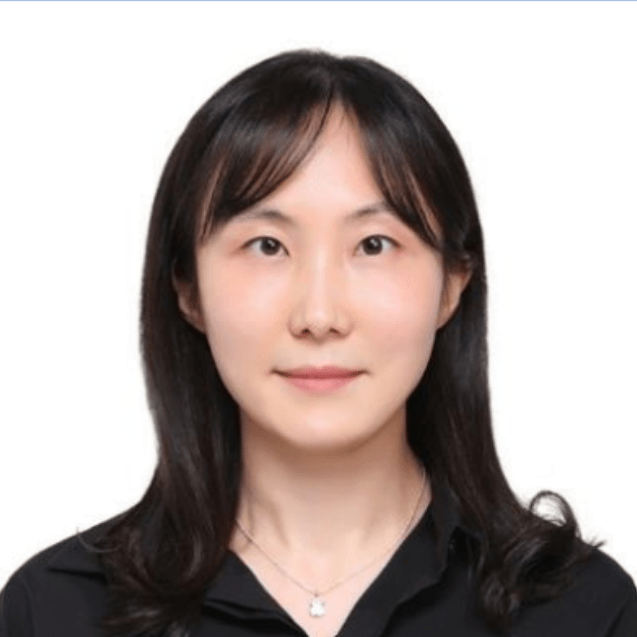
Acen Kevin (Daniela) is the Founder and Executive Director of the Itinga Charity Education Foundation (ICEF) and Director of St. Mary Goretti Secondary School Ngetta in Northern Uganda. Holding a Bachelor’s degree in Accounting and Finance, Kevin spearheads initiatives that deliver inclusive education to students with and without disabilities, including learners who are blind or physically challenged. Under her leadership, ICEF partnered to establish the region’s first inclusive secondary school, now serving 45 students from across Uganda. She drives accessibility through scholarships, assistive technologies, and inclusive teacher training. As Board Chair of the school’s academic committee, Kevin is dedicated to upholding quality and equity in education. In 2025, she was awarded the MTN Changemaker Grant for her groundbreaking work in assistive learning. Kevin is deeply passionate about creating a future where all learners— regardless of ability—have the opportunity to thrive. Donation/Support link

Isrina School; Linktree
Lagos Nigeria
Highlight: Spearheading the “Recycles Pay” project at Isrina School which empowers parents to offset children’s fees by generating income from recyclable materials
Year founded: 2016
Grades served: K-6
School vision: A world where every child, regardless of their economic background has equal access to quality education
Grace is a fervent champion of inclusive education, dedicating herself to this cause since the age of 15. Fueled by her personal experiences, she remains resolute in her mission to guarantee equitable access to quality education for every child, irrespective of their background. Notably, she advocates for environmental sustainability and spearheads the innovative “Recycles Pay” project, empowering parents to offset their children’s fees through the use of recyclable materials. With her certification as a Microsoft Educator, Grace actively pursues the enhancement of learning experiences and seeks to broaden educational access, aiming to disrupt the cycle of poverty through the delivery of high-quality education. Donation/Support link

Tsion Academy
Ile-Ife, Osun state, Nigeria
Highlight: Focused on providing free, quality education to out-of-school children in underserved communities using a personal and scalable funding model called the “Big Brother or Sister where each child is matched with a “Big Brother or Sister”—an individual donor who would commit to supporting the child’s education monthly or by term.
Year Founded: 2022
Grade: Nursery/Pre-Primary/Primary/Secondary
School Vision: To restore dignity, build character, and equip each child with the tools they need to thrive academically, emotionally, and socially.
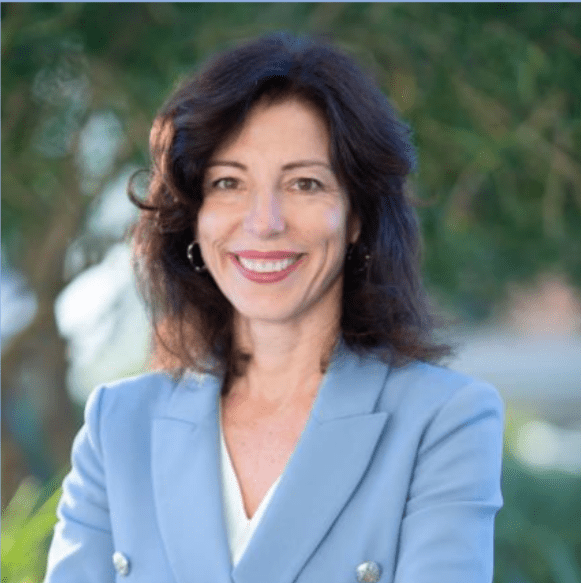
Adeola Tolulope Abayomi is the Founder and Executive Director of Tsion Academy, a free school for out-of-school children in Ile-Ife, Nigeria. A trained lawyer (LLB, BL) and the visionary force behind Evolufy Africa. Tsion Academy currently serves over 140 children aged 4 to 13, delivering quality, inclusive education to underserved communities. Through Evolufy Africa’s two branches—Tsion Academy and Maendeleo Africa— Adeola advances access, equity, and youth empowerment. She is passionate about building sustainable, replicable school models that drive genuine transformation. Her work bridges grassroots action and systemic change, offering hope and opportunity to the next generation of African leaders. Donation/Support link

Smart Bilingual Academy
Fatick, Senegal
Highlight: Creating equitable education access to students in second cities.
Year founded: 2022
Grades served: K-6
School vision: All children reach their full-potential and are agents of change in their schools, communities and the world.
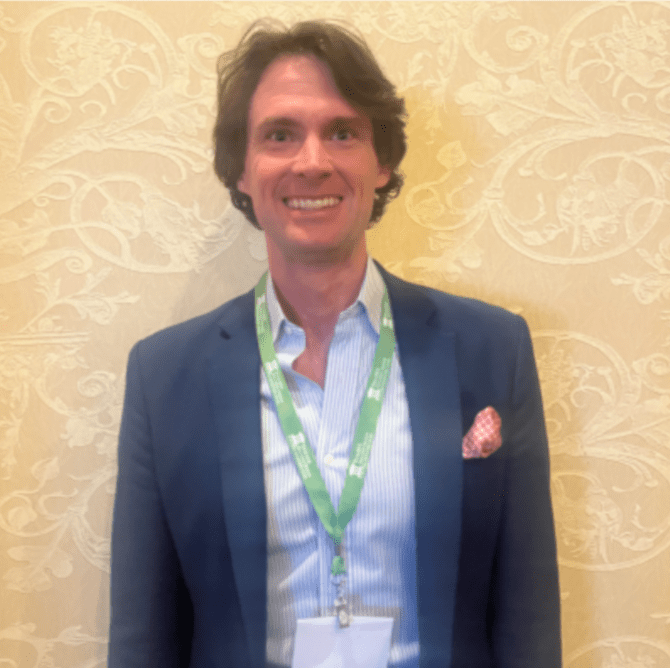
With a remarkable 15-year background in supporting social innovations, Tchanlandjou has been instrumental in mapping key actors and organizations within ecosystems for collective systemic impact. Since joining Ashoka in 2013, he has held the pivotal role of Regional Director for the Sahel region, where his strategic vision and ability to inspire and mobilize diverse partners have yielded significant accomplishments. Notably, Tchanlandjou spearheaded the creation of the Education and Youth Clusters, pivotal initiatives that have greatly enhanced Ashoka’s impact in the Sahel. In 2016, he further demonstrated his entrepreneurial spirit by founding ‘SeddoInvest,’ a start-up focused on identifying and preparing a pipeline of young social ventures and attracting investments to accelerate their development. He founded SBA after seeing first-hand the profound disparity between the quality of education available to students in Dakar, and in rural and per-urban areas in Senegal. Donation/Support link